+86-531-88239557
-
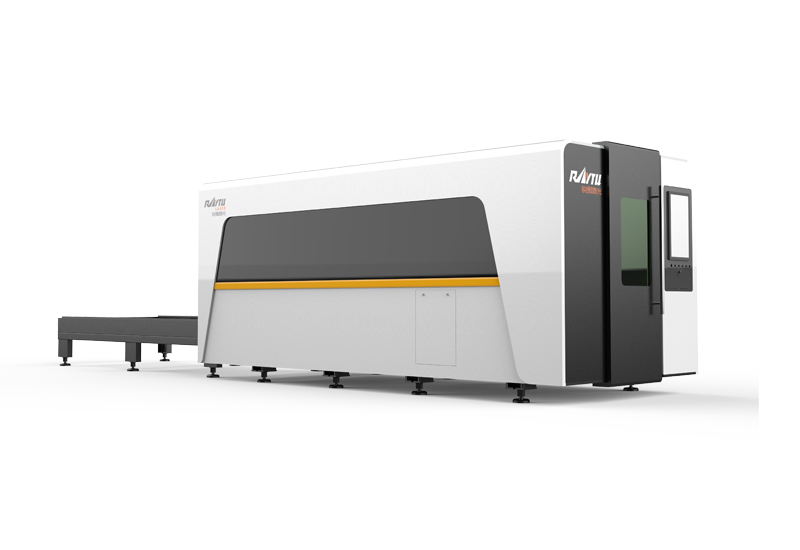 High Power Fiber Laser Cutting Machine
High Power Fiber Laser Cutting Machine
-
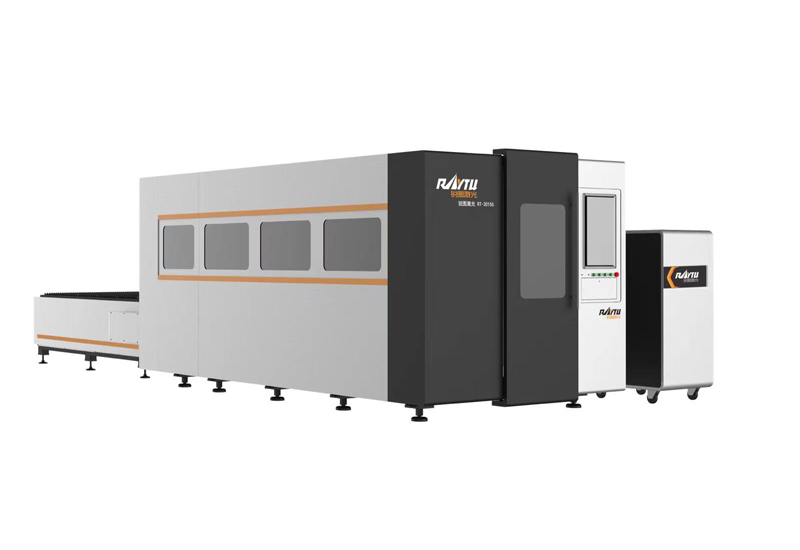 Enclosed Fiber Laser Cutting Machine
Enclosed Fiber Laser Cutting Machine
-
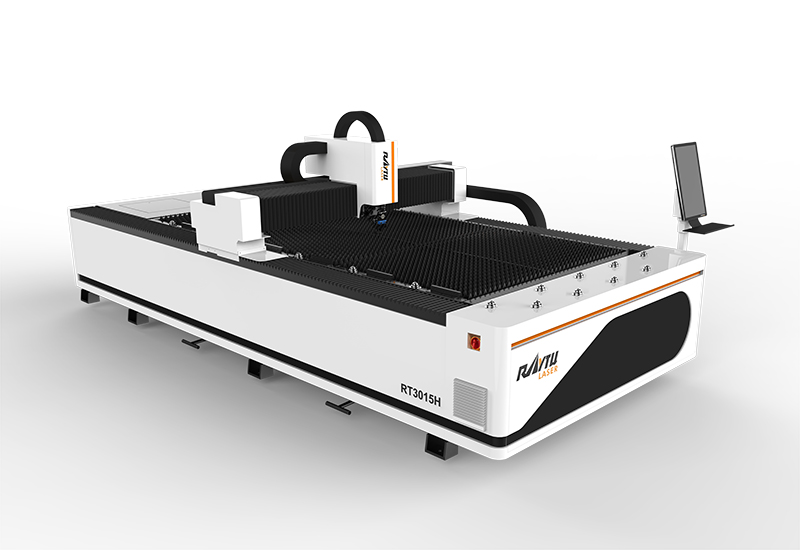 Sheet Metal Laser Cutting Machine
Sheet Metal Laser Cutting Machine
-
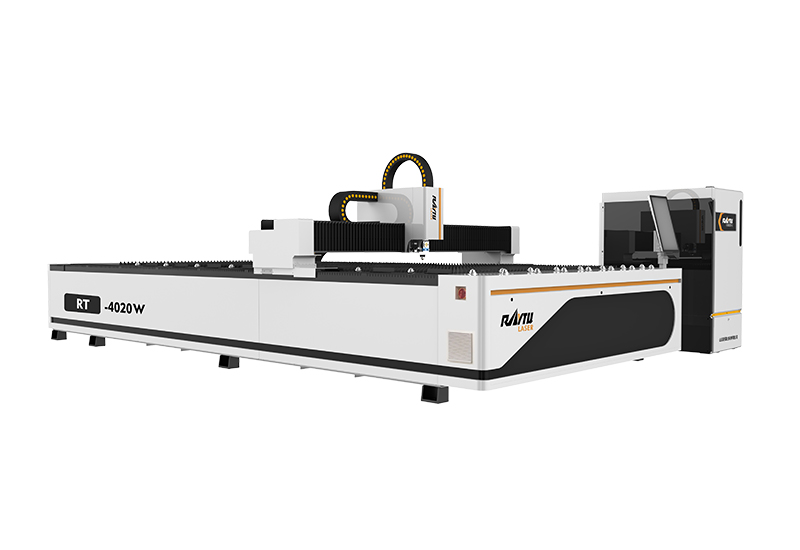 Medium Power Metal Laser Cutting Machine
Medium Power Metal Laser Cutting Machine
-
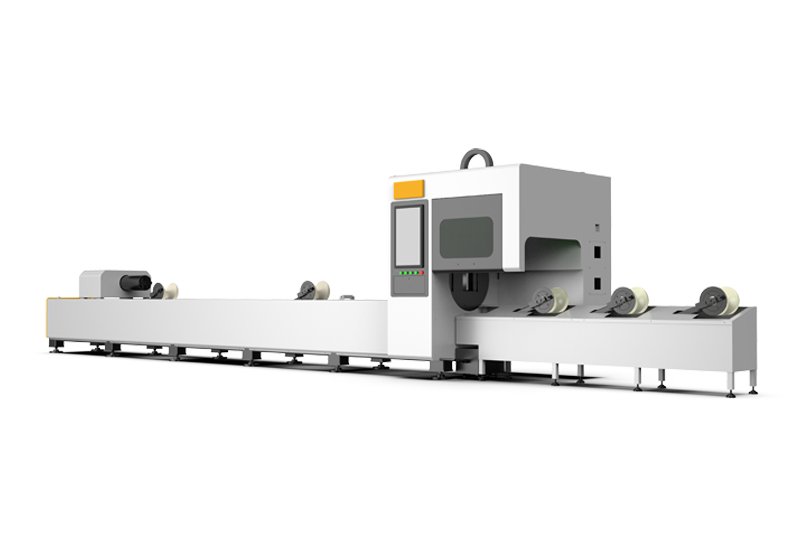 Automatic Tube Laser Cutting Machine
Automatic Tube Laser Cutting Machine
-
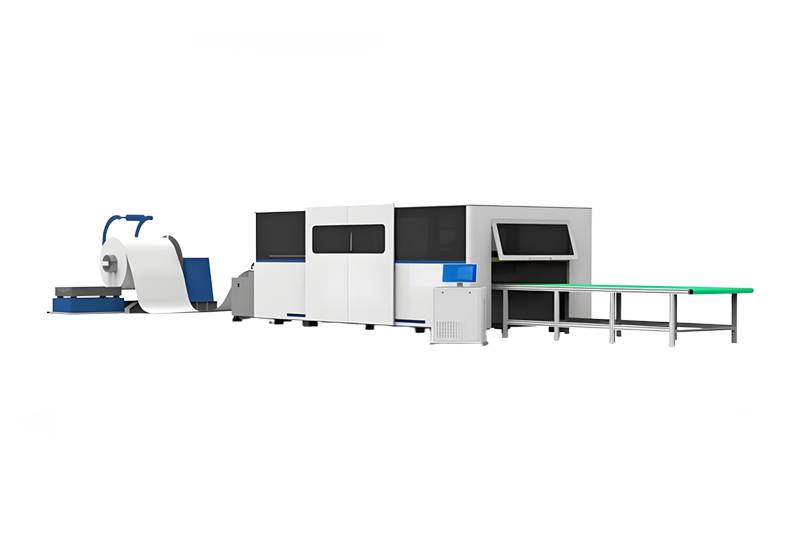 Coil Fiber Laser Cutting Machine
Coil Fiber Laser Cutting Machine
-
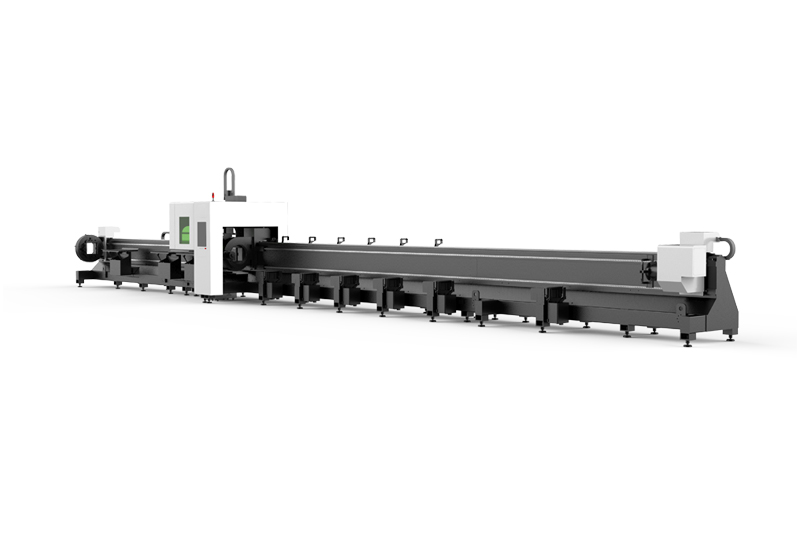 RTC-12036M 3 Chucks Tubeeber Laser Cutting Machine
RTC-12036M 3 Chucks Tubeeber Laser Cutting Machine
-
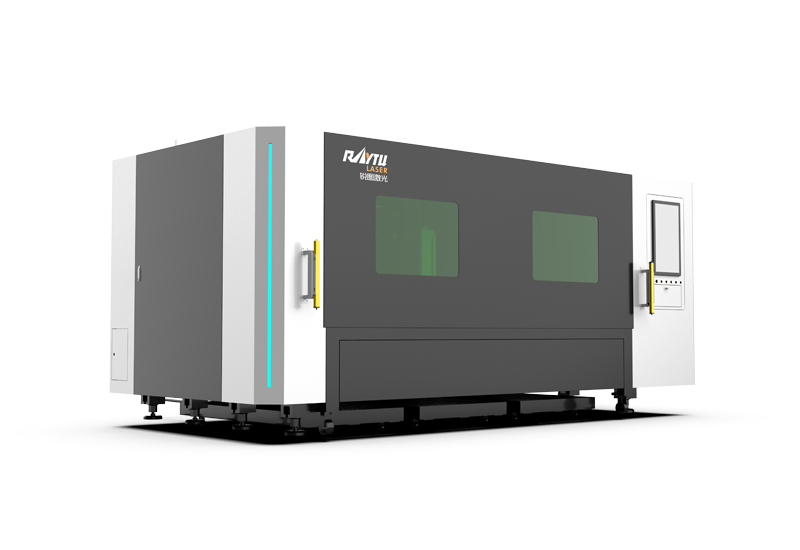 Single Table Enclosed Fiber Laser Cutting Machine
Single Table Enclosed Fiber Laser Cutting Machine





 EN
EN ES
ES RU
RU AR
AR